Automic Automation Intelligence Architecture
Knowing the different components of Automic Automation Intelligence (AAI) and understanding theirs interactions with your workload automation software is essential to setting up your system successfully. This page gives you an overview of the recommended Automic Automation Intelligence (AAI) architecture.
Overview
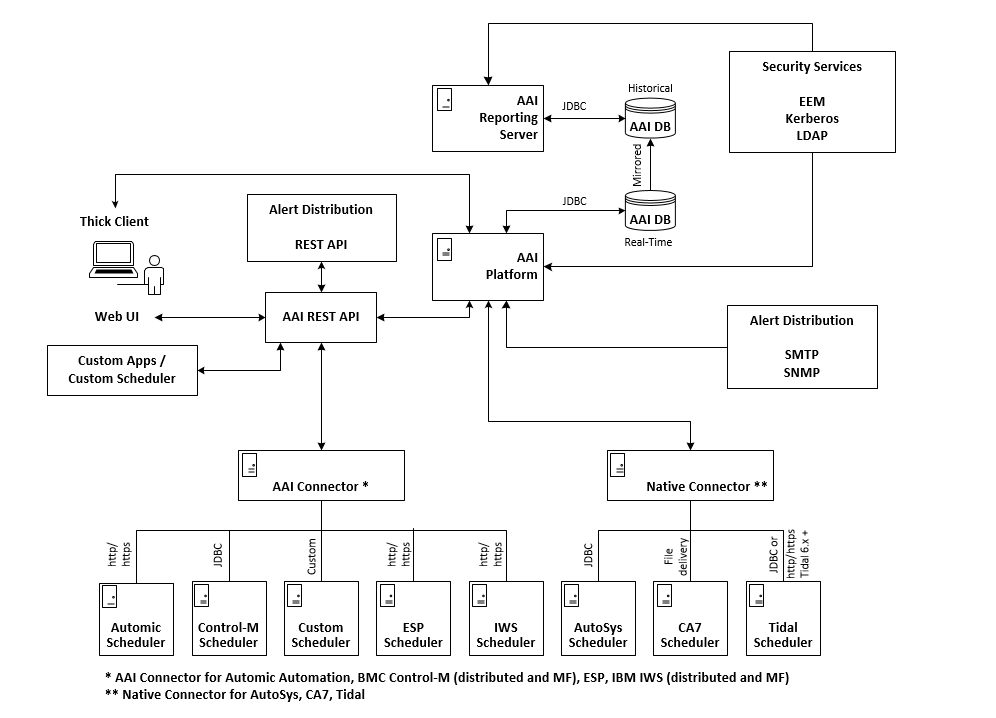
The Automic Automation Intelligence system main components are the database, the AAI Platform and the AAI Reporting Server:
-
AAI Database (Real-time and Historical): It is the central repository for all data such as the job definitions and event data from the workload automation engines, and any other data generated by AAI.
For performance reasons, it is recommended to use two instances of the database. The historical database instance is an identical copy of the real-time database instance, created via mirroring. The real-time database instance is used by the AAI Platform for persisting scheduler data in real-time. The AAI Reporting Server uses the historical database instance for generating reports.
-
AAI Platform: It is where all processing scheduler data takes place. This includes interpreting job definitions and event data from the workload automation engines, persisting information in the real-time AAI database instance, maintaining prediction models, updating jobstreams, generating alerts, and servicing user interfaces.
-
AAI Reporting Server: It supports customizing of visual dashboards, generating file-based reports in many formats (such as PDF, CSV, Word, and PowerPoint) scheduling of automatically generated reports, distributing reports via email, externalizing reports via URL, and building of custom reports with an ad-hoc report builder. The AAI Reporting Server uses the historical AAI database instance as a data source.
Once you have the Automic Automation Intelligence system in place, you need a Connector to integrate AAI with your scheduler.
It is recommended installing the connector on a dedicated machine. However, if you need more than one Connector, you can install them on the same machine.
Schedulers such as Automic Automation, Control-M (main frame and distributed), ESP, IWS (main frame and distributed), as well as custom schedulers require a separate AAI connector for the integration. These connectors communicate with the AAI Platform through the AAI REST API.
Connectors for AutoSys, CA7 and Tidal are built into the AAI Platform. They do not require a separate AAI connector component for the integration.
The connection type between the connector and the scheduler depends on the scheduler type. For more information, see Workload Automation / Scheduler Integration through Connectors.
Automic Automation Intelligence uses domains to configure security for user logins, authentication method and access privileges to AAI's functions. You can either use the AAI native security model, or integrate security services via eEM, Kerberos, and LDAP to your system. For more information, see Domains.
You can also set up your alert distribution over SNMP and SMTP protocols, or through the AAI REST API.
See also: